Join the next generation of Quantity Surveyors who are redefining sustainability through smart cost control and digital precision. From cutting waste to planning greener projects with BIM, your skills can shape a cleaner, more efficient Malaysia.
{{ vm.tagsGroup }}
21 Jul 2025
8 Min Read
Dr Soon Lam Tatt (Academic Columnist)
Imagine a bustling construction site in Malaysia—the heartbeat of the nation’s rapid urban expansion. As buildings rise, so too do the mountains of discarded materials: broken bricks, surplus concrete, warped timber. Each year, Malaysia produces an estimated 8 million tonnes of construction waste. The bulk of it ends up in landfills or, worse, is illegally dumped—polluting our environment and endangering public health.
This is no small issue. Harmful substances leaching from waste sites can contaminate soil, poison rivers, and degrade air quality. Yet despite mounting environmental costs, landfill remains the industry’s go-to disposal method. With limited landfill space and inadequate recycling infrastructure, Malaysia’s construction sector faces a critical challenge.
To address it, we need more than incremental improvements. We need to rethink how we build—and how we manage waste—from the outset. This is where Building Information Modelling (BIM) comes into play.
Construction waste is rarely the result of a single oversight. It accumulates for many reasons—miscalculations in material orders, last-minute design changes, inefficient storage, and a lack of training in sustainable practices.
Every stage of a construction project—design, procurement, building—offers opportunities for waste to sneak in. Without better planning and foresight, this waste spirals out of control.
To manage construction waste effectively, we need to understand what we’re dealing with:
When hazardous and non-hazardous waste are mixed, recycling becomes far more complicated. That’s why source separation is essential.
For many construction sites, waste management is a logistical headache. Tracking waste accurately is difficult without digital support, and without trained teams or clear processes, valuable materials often end up in landfills.
Systemic issues add to the challenge. Malaysia’s construction waste regulations are still evolving. Smaller companies, in particular, struggle with the costs of compliance and the lack of awareness around sustainable alternatives.
What the industry needs is a practical, scalable system that makes waste planning and reduction an integral part of the build—not an afterthought. This is where digital platforms like BIM offer real value.
Building Information Modelling is far more than a 3D design tool. It’s a digital ecosystem that connects every stakeholder in a construction project—from architects and engineers to contractors and facility managers.
By developing a virtual model of the entire project, BIM enables teams to identify potential issues early, optimise material usage, reduce costly rework, and streamline collaboration.
In essence, BIM brings efficiency and sustainability to the forefront of the construction process.
Here’s how BIM supports sustainable construction:
With BIM, sustainability is no longer a bolt-on—it’s embedded into the blueprint.
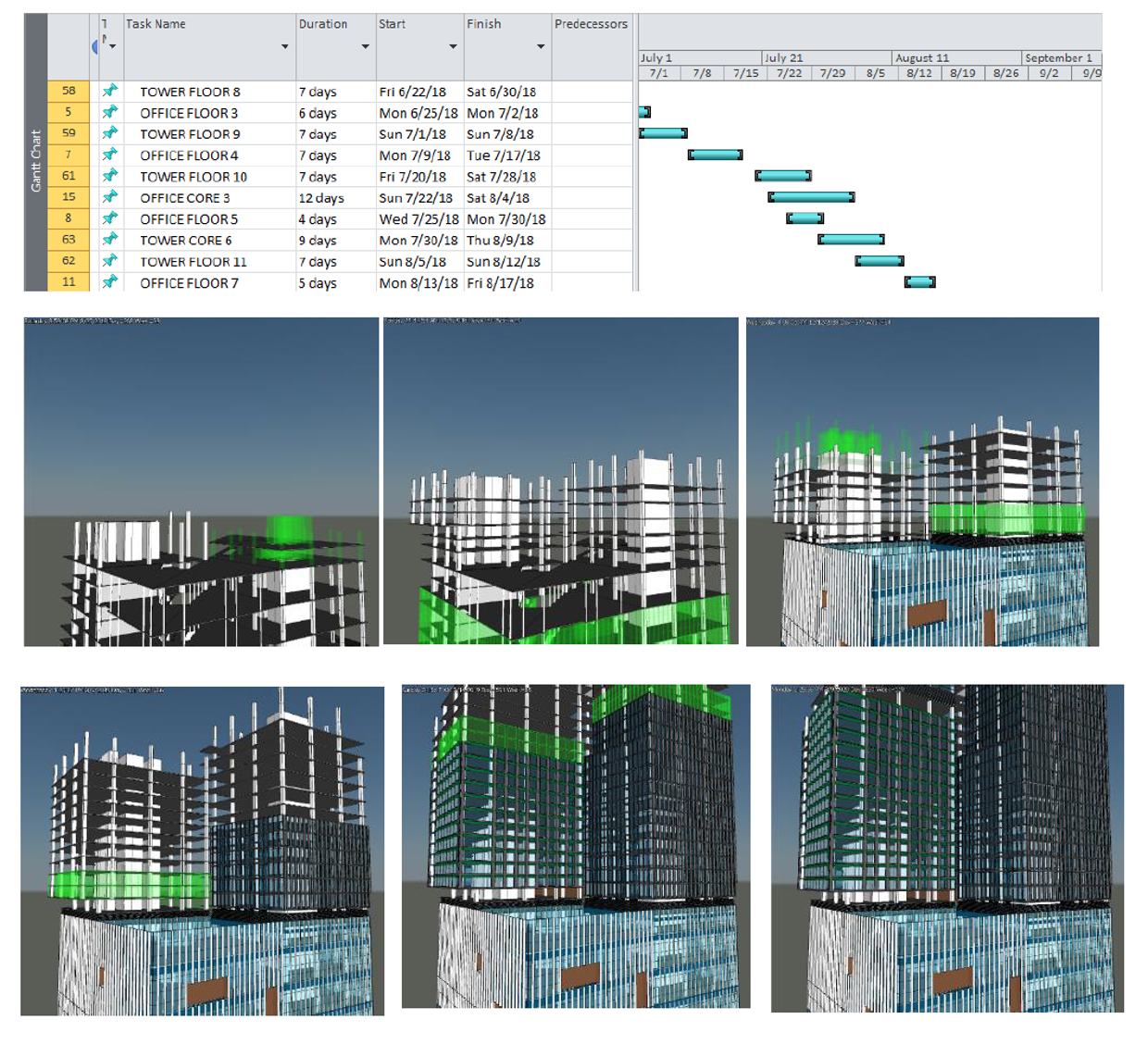
With 4D BIM, teams gain a visual schedule of the entire project. It doesn’t just show what the build will look like—it shows when and how each stage happens.
Benefits include:
4D BIM reveals more than just the structure—it maps the journey. By connecting a 3D model with your construction timeline, 4D BIM visualises how a project unfolds step by step. It empowers teams to anticipate delays, fine-tune logistics, and build with greater confidence right from the start. Image Source: Autodesk
| BIM Level | Focus | Function | Why It Matters | How It Helps |
| 3D BIM | Visualisation | View full project design | Catch errors early | Better design accuracy |
| 4D BIM | Time & Scheduling | Link construction tasks to a timeline | Avoid delays | Improve project flow |
| 5D BIM | Cost Estimation | Tie materials to real-time pricing | Manage budgets effectively | Minimise financial risk |
| 6D BIM | Sustainability | Monitor energy and material use | Make informed eco-decisions | Lower environmental impact |
| 7D BIM | Facilities Management | Plan maintenance post-build | Enhance operational efficiency | Extend building lifespan |
BIM directly supports waste minimisation strategies through improved planning and real-time oversight.
Despite its advantages, BIM adoption in Malaysia remains limited. Key barriers include:
To drive widespread use of BIM in Malaysia’s construction industry, several steps are vital:
BIM represents more than just technological advancement—it’s a catalyst for systemic change. When used to its full potential, it can reduce construction waste by up to 15%, improve timelines and budgets, and contribute meaningfully to environmental protection.
For Malaysia to move towards a more sustainable built environment, BIM must be at the centre of that journey. The future of construction lies not just in building smarter, but in building with intention, where sustainability and efficiency go hand in hand.
Let’s not just imagine a greener Malaysia. Let’s build it—digitally, deliberately, and sustainably.
Join the next generation of Quantity Surveyors who are redefining sustainability through smart cost control and digital precision. From cutting waste to planning greener projects with BIM, your skills can shape a cleaner, more efficient Malaysia.