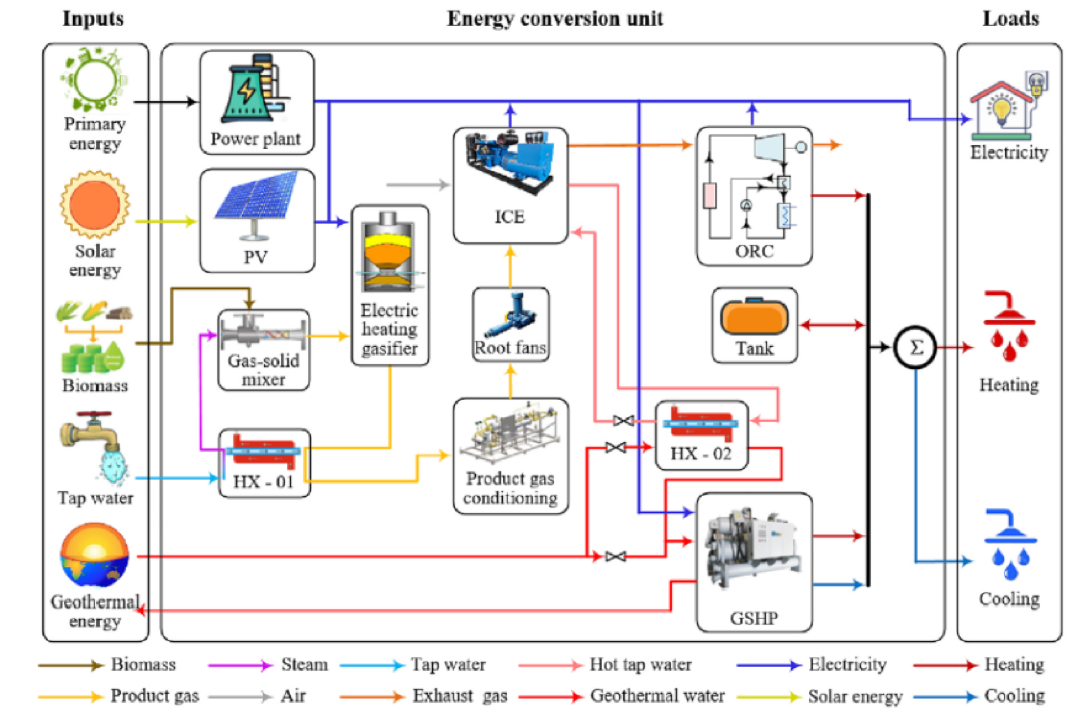
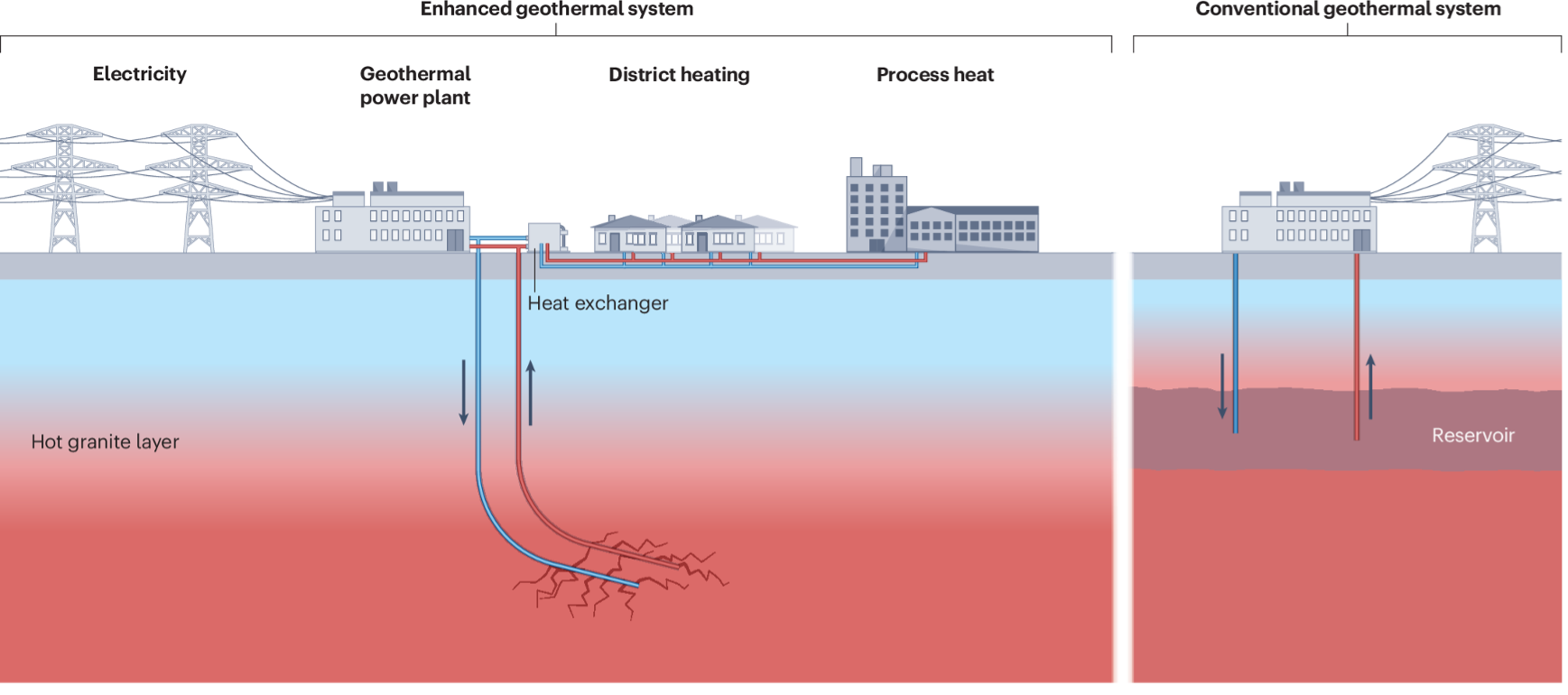
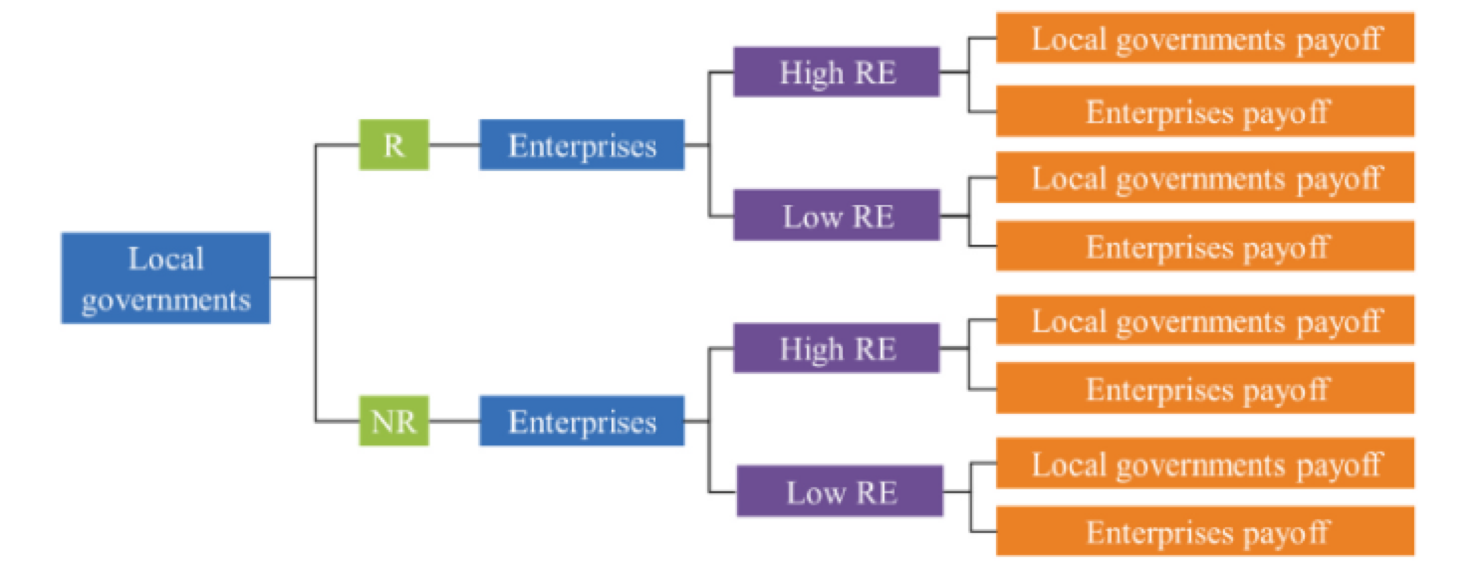
Despite significant progress, full-scale clean energy adoption still faces challenges, particularly due to the high upfront investment needed for renewable energy infrastructure. While the long-term benefits outweigh the costs, this remains a major barrier, especially for governments and companies in developing nations.
Intermittency and grid reliability continue to be key concerns. The variability of solar and wind energy calls for large-scale storage systems and infrastructure upgrades. Decentralized energy systems and smart grid technologies will be crucial in solving these issues.
The transition also requires improvements in raw material procurement and supply chain management. Lithium, cobalt, rare earth elements, and other minerals vital for batteries, solar panels, and wind turbines are often sources of geopolitical tension and environmental concerns. Sustainable mining and recycling practices must be integrated to tackle these challenges.
Ultimately, policy and regulatory frameworks must evolve to promote renewable energy adoption. Governments must create incentives, subsidies, and clear legislative frameworks to drive investment, requiring coordinated efforts from governments, businesses, and researchers to accelerate the transition.
What’s Waiting for You
As renewable technologies continue to advance, your skills as a future engineer or energy professional will be more important than ever. The demand for people likes you—those who can tackle challenges in energy storage, optimise smart grids, and design sustainable infrastructure—is growing.
You’ll also can drive change beyond the lab or design studio. By helping industries adopt smarter energy solutions—whether through digital tools for grid management or cleaner industrial processes—you’ll be part of something bigger. And by embracing new ideas like circular economy models and collaborating across fields, you’ll be helping to accelerate the global shift toward a cleaner, more resilient future.